Harnessing the sun's energy is a powerful step towards sustainability and energy independence. With the rising costs of electricity and growing concerns about climate change, investing in a solar power system is becoming increasingly attractive. However, the efficiency of your system hinges on careful planning and design; a poorly conceived setup can significantly reduce your energy savings and return on investment. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to optimize your solar power potential, ensuring you maximize your energy generation and minimize wasted resources.
This comprehensive guide explores every facet of efficient solar system design, from initial site assessment and panel selection to optimal placement and system integration. We will provide a step-by-step process to help you navigate the complexities of building a high-performing, cost-effective solar power system that will meet your energy needs for years to come. Follow along as we uncover the secrets to maximizing your solar energy harvest.
Preparation and Safety Guidelines
- Solar Panels
- Inverters (Micro or String, depending on needs)
- Batteries (Optional, especially for off-grid)
- PV Combiner Box/Circuit Breakers
- Wiring (Outdoor-rated or THHN/THWN in conduit)
- MC4 Connectors
- Heavy Gauge Wire & Lugs (for batteries)
- Always engage a qualified and licensed electrician for all aspects of solar panel installation and system maintenance. Improper wiring or handling can lead to serious injury or fire.
- Never touch or approach any part of the solar panel system during a storm or inclement weather. Electricity from a damaged system can be lethal.
- Ensure your solar system is properly grounded to prevent electrical surges and potential hazards. Regularly inspect grounding connections for corrosion or damage.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Solar Panel Selection
- Select panels with higher wattage output per area for maximum energy generation, considering your budget and available roof space.

Solar Panel Selection Inverter Selection
- Consider both micro-inverters (for individual panel monitoring and better shade tolerance) and string inverters (for cost-effectiveness in large, unshaded arrays). The choice depends on your specific needs and system size.

Inverter Selection Battery Configuration (if applicable)
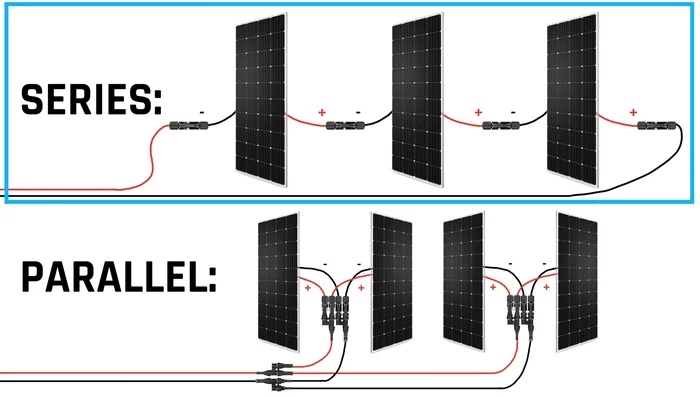
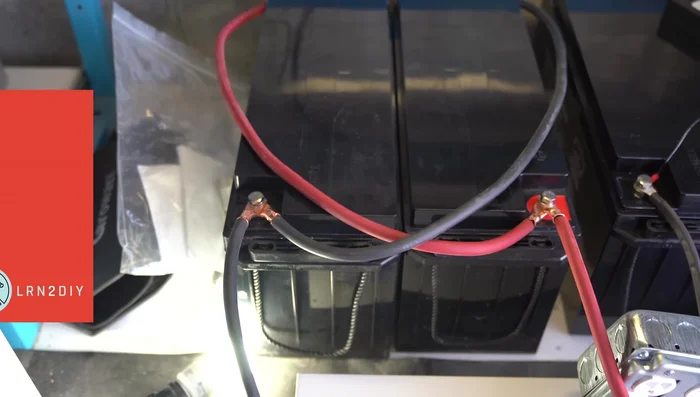
- For batteries, connecting in series adds voltage, while parallel adds amperage. Choose the configuration that matches your inverter's voltage requirements and desired amp-hour capacity. (See 'SUAVE' mnemonic for remembering which adds what).

Battery Configuration (if applicable) Safety and Protection
- Use PV combiner boxes, circuit breakers, and disconnects to isolate sections of your system for maintenance and provide overload protection. Adhere to all local electrical codes and guidelines.

Safety and Protection Battery Selection (if applicable)
- If off-grid, batteries are essential. Choose based on voltage, amp-hour capacity, and cycle life. For grid-tied systems with backup power, consider options like Tesla Powerwall or other suitable battery solutions.

Battery Selection (if applicable) Wiring and Connections
- Employ outdoor-rated wiring or THHN/THWN in conduit for external runs. Utilize MC4 connectors for solar panels and heavy-gauge wire with appropriate lugs for batteries.

Wiring and Connections
Read more: Harnessing Solar Power: A Green Energy Solution
Tips
- Consider bifacial panels to increase power output by up to 30% by capturing light from both sides.
- For grid-tied systems with backup power capabilities, disconnect the system from the grid to prioritize home power during outages.
- Use the 'SUAVE' mnemonic to remember series adds volts, parallel adds amps.
- Always have a certified electrician inspect and approve your work before energizing the system.