The global shift towards renewable energy sources is undeniable, demanding a workforce equipped with the knowledge and skills to build and maintain these crucial technologies. Effective education is paramount, but traditional classroom learning often lacks the hands-on experience necessary for true comprehension. This article explores a novel and engaging approach to renewable energy education: the model car project. By building and modifying small-scale model cars powered by renewable energy sources, students gain practical experience with fundamental principles of solar, wind, and even hydro-electric power generation.
This practical, project-based learning method allows students to actively experiment with different designs, materials, and energy sources, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This step-by-step guide will detail the construction of a model car powered by renewable energy, from initial design and material selection to testing and optimization, showcasing the exciting possibilities of this innovative educational approach.
Preparation and Safety Guidelines
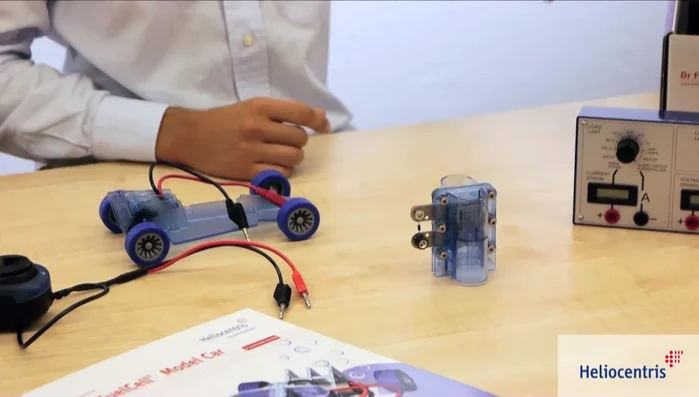
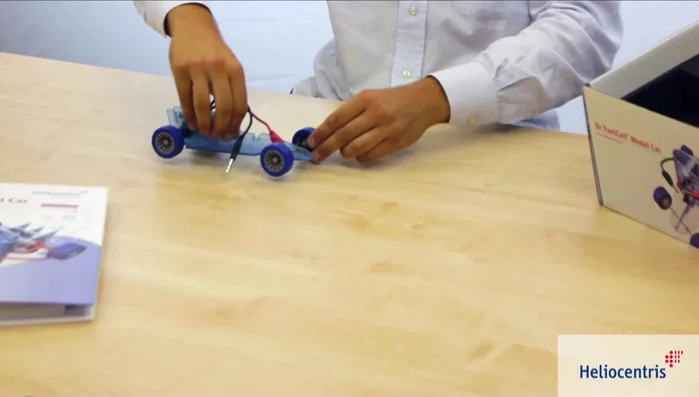
- Model car
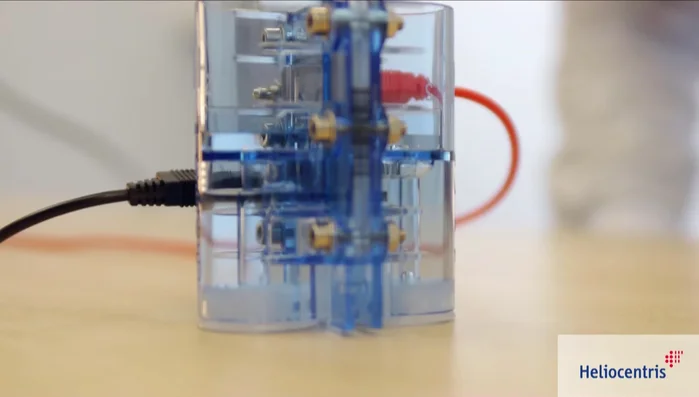
- Fuel cell
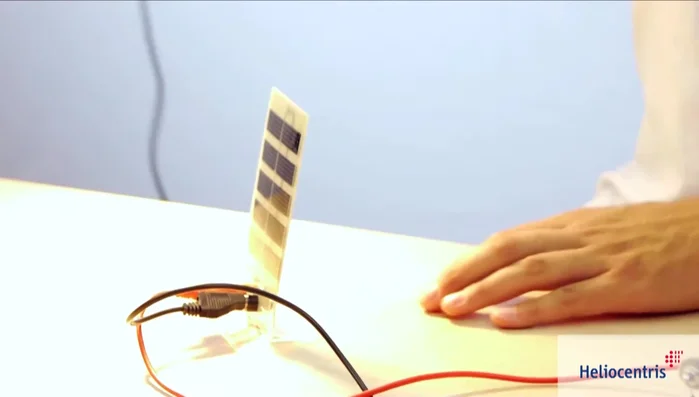
- Solar panel
- Hand generator
- Electrolyzer
- Photovoltaic module
- Load measurement box
- Distilled water
- Cables
- Stopwatch
- User manual
- Teacher's guide
- Always supervise children when handling tools, batteries, and small parts. Improper use can lead to injury.
- Ensure adequate ventilation when using any materials that might produce fumes or gases. Work in a well-ventilated area or outdoors.
- Dispose of batteries and other components responsibly according to local regulations. Do not throw them in the trash.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Introduction and Setup
- Introduce renewable energy concepts using a model car.
- Power the model car with a fuel cell or solar panel (emission-free).
- Use the model car's components (chassis, axis, photovoltaic module) to understand the system.



Introduction and Setup Solar Power Operation
- Operate the car using solar energy (photovoltaic module).

Solar Power Operation Alternative Power Source (Hand Generator)
- Alternatively, use the hand generator to produce electricity.

Alternative Power Source (Hand Generator) Fuel Cell Operation
- Utilize the reversible PEM fuel cell (acting as both fuel cell and electrolyzer).
- Generate hydrogen and oxygen using the electrolyzer and store them temporarily.
- Consume the stored hydrogen and oxygen in the fuel cell to generate electricity and power the car.



Fuel Cell Operation Hands-on Experiments and Data Collection
- Conduct practical experiments to understand how renewable energy technologies work.
- Illustrate the relationships between production, conversion, storage, and consumption of renewable energy.
- Use the load measurement box with integrated consumers (motor, lamp) to conduct experiments and measure characteristic curves.



Hands-on Experiments and Data Collection Lesson Planning and Implementation
- Use the provided teaching materials (user manual, teacher's guide) to conduct experiments and lessons effectively.

Lesson Planning and Implementation
Read more: Harnessing Solar Power: A Green Energy Solution
Tips
- The model car facilitates hands-on learning and makes science curricular fun.
- The model car's easy-to-use design and robust components ensure high-quality experiments.
- The teacher's guide provides learning objectives, teaching methods, and Q&A for effective lesson preparation.
- The student section includes experimental setup templates and tasks to collect measurement data.